World’s First Human Death from H5N5 Bird Flu Reported in the U.S.
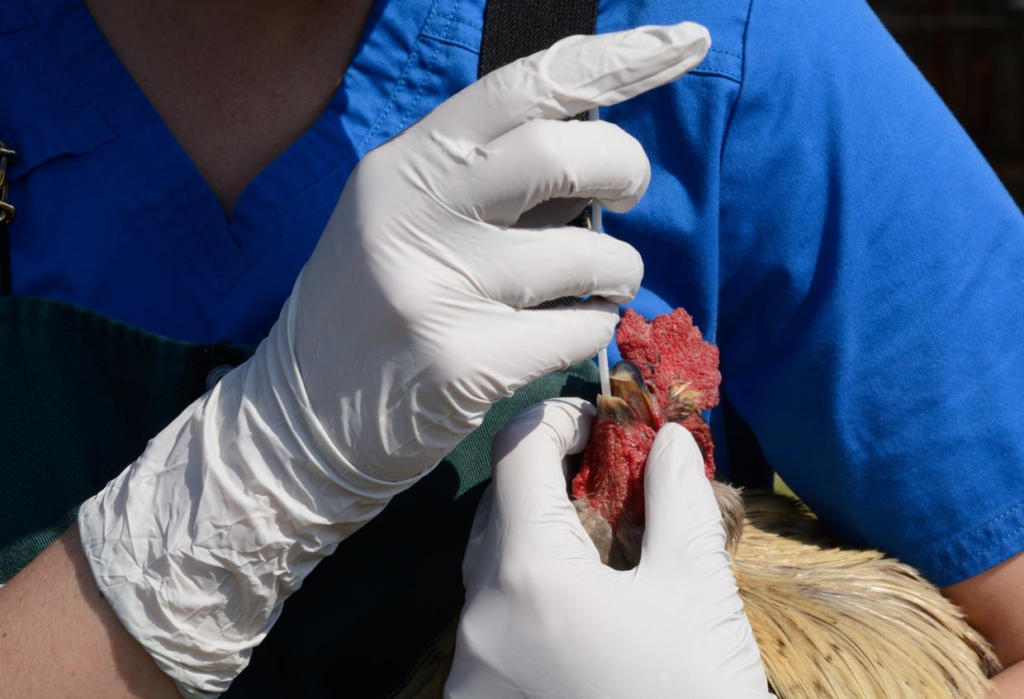
Health officials in Washington State have confirmed that a Washington resident has died from the H5N5 avian influenza strain, marking the first recorded case of human death associated with this rare bird flu variant. The individual, who had pre-existing health conditions, was hospitalized earlier in November before being diagnosed with the infection. Laboratory testing by the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) confirmed that the virus involved was influenza A(H5N5), a subtype of bird flu previously only detected in wild birds and some mammals.
The infection likely occurred after the person had direct contact with infected wild birds or domestic poultry. This connection was supported by the detection of the avian flu virus in environmental samples collected near the person’s poultry flock. However, health authorities have reassured the public that there is no evidence of human-to-human transmission at this point.
Despite the fatality, experts emphasize that the risk to the general public remains low. The CDC and other health agencies continue to monitor the situation closely, including tracking potential cases among those who may have had contact with infected birds. For now, proper precautions like wearing protective gear when handling birds, avoiding contact with sick or dead birds, and practicing good hygiene are advised for those at risk.
While the H5N5 virus is concerning, it is part of the broader surveillance efforts to monitor how avian influenza strains evolve and pose threats to human health. With continued vigilance, health officials hope to prevent a larger outbreak.
Understanding H5N5: What Scientists Know About the New Bird Flu Case

The recent confirmation of a human death linked to the H5N5 avian influenza strain has triggered extensive scientific analysis. Influenza A(H5N5) has historically been detected in bird populations worldwide, often in migratory birds and poultry, but it has rarely infected mammals. This Washington State case marks a crucial turning point in how researchers view the virus’s potential to cross species barriers.
Laboratory genetic sequencing is underway to better understand the virus that caused the infection. Scientists are comparing the H5N5 strain from this human case with variants found in local bird populations to see if any genetic changes could have facilitated infection in a human host. The goal is to determine whether the virus has evolved features that allow it to bind more effectively to human respiratory receptors.
Health experts stress that, although this is a serious case, there is currently no sign that H5N5 can infect people easily or spread from person to person. This dramatically limits the likelihood of widespread outbreaks. Instead, the case highlights the need for vigilance in monitoring influenza viruses that circulate in animal reservoirs.
Bird flu viruses are known to mutate rapidly, which is why global surveillance systems track changes in viral genomes across species. This monitoring helps public health officials anticipate potential threats and prepare vaccines or response strategies if needed.
People who live near or care for birds should follow established safety guidelines, including avoiding direct contact with sick or dead birds, wearing gloves and masks when necessary, and practicing good hygiene to reduce the risk of infection.
This event provides a valuable opportunity for the scientific community to expand its understanding of avian influenza and strengthen global preparedness.
Game Changer: Toyota Unveils First Solid-State EV Batteries with 9-Minute Charging and 745-Mile Range
Toyota has taken a giant leap forward in the EV revolution with the announcement of its first solid-state batteries designed for electric vehicles. These next-generation batteries promise to deliver rapid charging times and long-range driving that could put current lithium-ion batteries to shame.
The new solid-state batteries can be charged to 80% in just 9 minutes, a dramatic improvement over the 30-60 minutes it currently takes to charge most electric vehicles on fast chargers. This breakthrough could make long trips much easier and less time-consuming, addressing one of the most common concerns about EV adoption: charging time.
Additionally, these batteries boast an impressive range of 745 miles on a single charge, putting them far ahead of many of the top EV models on the market today. For context, most EVs currently top out at around 300-400 miles per charge, making this advancement an exciting prospect for anyone looking for more practicality in their electric vehicle.
Solid-state technology, which replaces the liquid electrolyte in traditional batteries with a solid electrolyte, is considered much safer and more efficient. It significantly reduces the risk of overheating and increases energy density, meaning a lighter, more powerful battery that is less likely to degrade over time. Toyota’s solid-state batteries are expected to hit the market by 2027, marking a major step toward mass adoption of electric cars.
With faster charging and longer driving ranges, Toyota’s solid-state battery technology could finally eliminate the major limitations that have hindered the widespread use of EVs. This is a true game changer for the automotive industry and a huge win for environmentally conscious consumers.
Tesla’s New 500-Mile Range EV: The Future of Long-Distance Electric Travel
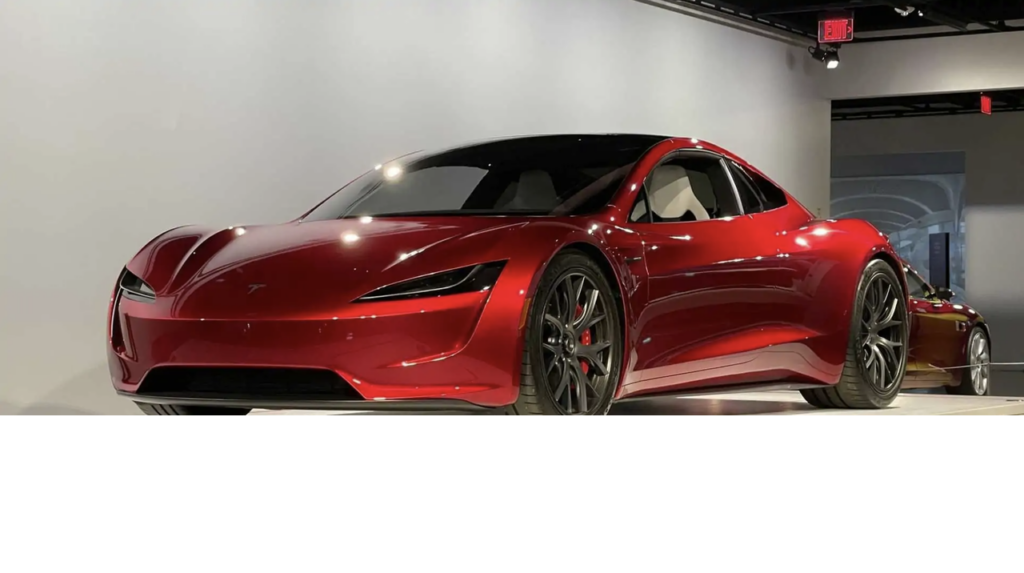

Tesla has taken the EV market by storm again with the launch of its latest electric vehicle that offers a 500-mile range on a single charge. This new achievement marks a major milestone for the electric vehicle industry, overcoming one of the biggest hurdles that EV owners face — range anxiety. Tesla’s new vehicle has the potential to redefine how long-distance travel is approached in the EV world.
With the improved battery technology and energy-efficient design, this model can comfortably travel long distances without the need for frequent charging stops. The 500-mile range is more than double the average range of most electric vehicles on the market today, making it a game changer for road trips and cross-country travel. This breakthrough could be the key to eliminating concerns about finding charging stations in remote areas, opening up more opportunities for EVs to replace gas-powered cars.
The new Tesla EV also comes equipped with advanced autopilot systems, enhanced safety features, and a sleek new design that combines luxury with practicality. Tesla’s commitment to cutting-edge technology and sustainability is reflected in this car, which offers the ideal blend of performance, range, and environmental responsibility.
With an emphasis on fast-charging capabilities, Tesla’s 500-mile range EV could lead the way in making electric vehicles more accessible to the everyday driver while further pushing the automotive industry toward a fully electric future.
Google’s Quantum Computing Breakthrough: Solving Problems Once Thought Impossible
In a world where computing power is essential for innovation, Google has taken a giant leap forward with its latest quantum computing breakthrough. The company announced that it has successfully solved problems previously deemed impossible for traditional computers to tackle, using its new quantum processor.
Quantum computing operates on the principles of quantum mechanics, which allow it to perform complex calculations at speeds far beyond the capabilities of classical computers. Google’s new processor has demonstrated an ability to perform calculations that would take even the world’s fastest supercomputers millions of years to solve, within a fraction of the time.
This breakthrough opens the door to solving some of the most pressing issues in fields such as medicine, finance, material science, and artificial intelligence. From optimizing drug design to improving encryption security, quantum computing has the potential to revolutionize numerous industries.
Although still in the experimental phase, Google’s advancements in quantum computing bring the technology closer to mainstream use. The ability to solve problems previously thought impossible could accelerate scientific research, boost technological innovations, and create new possibilities that were once out of reach.
As Google continues to develop this technology, the potential applications are limitless. The world of computing is on the brink of a revolution, and Google is at the forefront, paving the way for the future of technology.
World’s First Carbon-Capture Facility Opens: A Major Milestone in Combating Climate Change
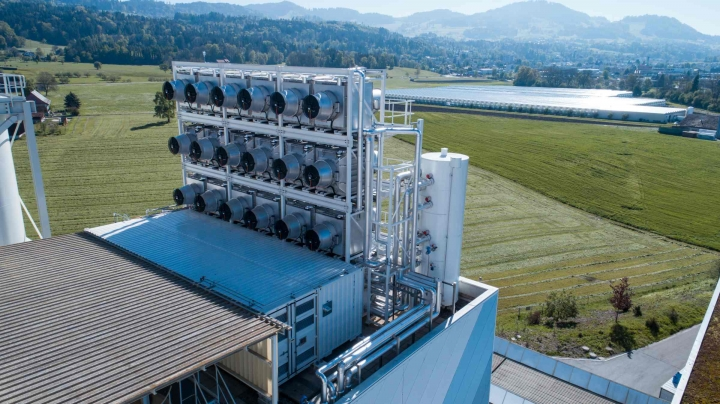

A groundbreaking carbon-capture facility has officially opened, representing a monumental step forward in the battle against climate change. This commercial-scale facility, located in the heart of the industrial world, will capture millions of tons of carbon dioxide every year and prevent it from entering the atmosphere, offering hope in the global efforts to fight global warming.
The facility works by capturing CO2 emissions produced by industrial processes, compressing them into a liquid form, and storing them safely underground. This technology, known as direct air capture (DAC), is one of the most promising solutions for reducing the planet’s carbon footprint. Once fully operational, the facility will have the capacity to remove over 1 million tons of CO2 annually, making a significant dent in the carbon emissions that drive climate change.
What makes this achievement particularly significant is the scale at which it is being deployed. For years, carbon-capture technology has been the subject of research and experimentation, but this is the first time it’s being implemented on a commercial level with the capacity to make a real impact.
Experts believe that the successful operation of this facility could pave the way for future global-scale carbon-capture projects that will be essential to meeting international climate goals. This is a key milestone in the race to achieve net-zero emissions and avoid the worst impacts of climate change.
The opening of the facility marks a turning point, showing that technology can play a vital role in mitigating environmental damage and creating a more sustainable future.
Microsoft’s AI-Powered Healthcare Solution Can Predict Diseases Years Before Symptoms Appear

Microsoft has unveiled a cutting-edge AI-powered healthcare solution that has the potential to revolutionize disease prediction and prevention. This groundbreaking technology uses artificial intelligence to analyze vast amounts of medical data, including patient records, genetic information, and lifestyle factors, to predict diseases years before symptoms even appear.
The AI system is capable of identifying patterns and correlations in patient data that are invisible to the human eye, making early predictions about conditions such as heart disease, diabetes, cancer, and more. This predictive capability could change the way doctors approach patient care, shifting from reactive treatment to proactive prevention.
By flagging potential health issues before they manifest, doctors can implement preventive measures, personalized treatments, and lifestyle changes that can significantly improve patient outcomes. For example, the system could identify early signs of heart disease and alert a patient to make dietary changes, exercise more, or begin medical interventions, drastically reducing the risk of heart attacks and other complications.
This technology is built upon years of data mining and AI research, and Microsoft is partnering with leading healthcare providers to integrate it into existing healthcare systems. The goal is to lower healthcare costs, improve diagnostic accuracy, and save lives by catching diseases early when they are most treatable.
With its ability to predict diseases years in advance, this AI-powered healthcare solution could change the face of modern medicine and create a healthier future for millions.
Game Changer: NASA Confirms Vast Underground Water on Mars

NASA has announced compelling new evidence suggesting that large quantities of liquid water may exist deep beneath the surface of Mars. Using advanced radar data and seismic measurements from multiple missions, scientists detected signals consistent with underground water reservoirs trapped beneath layers of rock and ice.
Mars was once a warm and wet planet, with rivers, lakes, and possibly oceans. Over billions of years, much of that surface water disappeared as the planet lost its atmosphere. However, this new discovery indicates that water did not vanish entirely—it may have retreated underground, where it could remain stable even in Mars’ harsh conditions.
The presence of subsurface water dramatically increases the possibility that microbial life could have survived on Mars. On Earth, life thrives deep underground, protected from radiation and extreme temperatures. Similar environments on Mars could offer the same protection.
For future human exploration, underground water would be a critical resource. It could be used for drinking, growing food, producing oxygen, and even creating rocket fuel. This discovery strengthens the case for long-term human presence on the Red Planet.
NASA scientists caution that drilling to confirm these reservoirs will be extremely challenging, but the findings mark one of the most important steps toward understanding Mars’ hidden interior. Mars is no longer just a dry, dead world—it may still be quietly holding the ingredients for life.




Leave a Comment